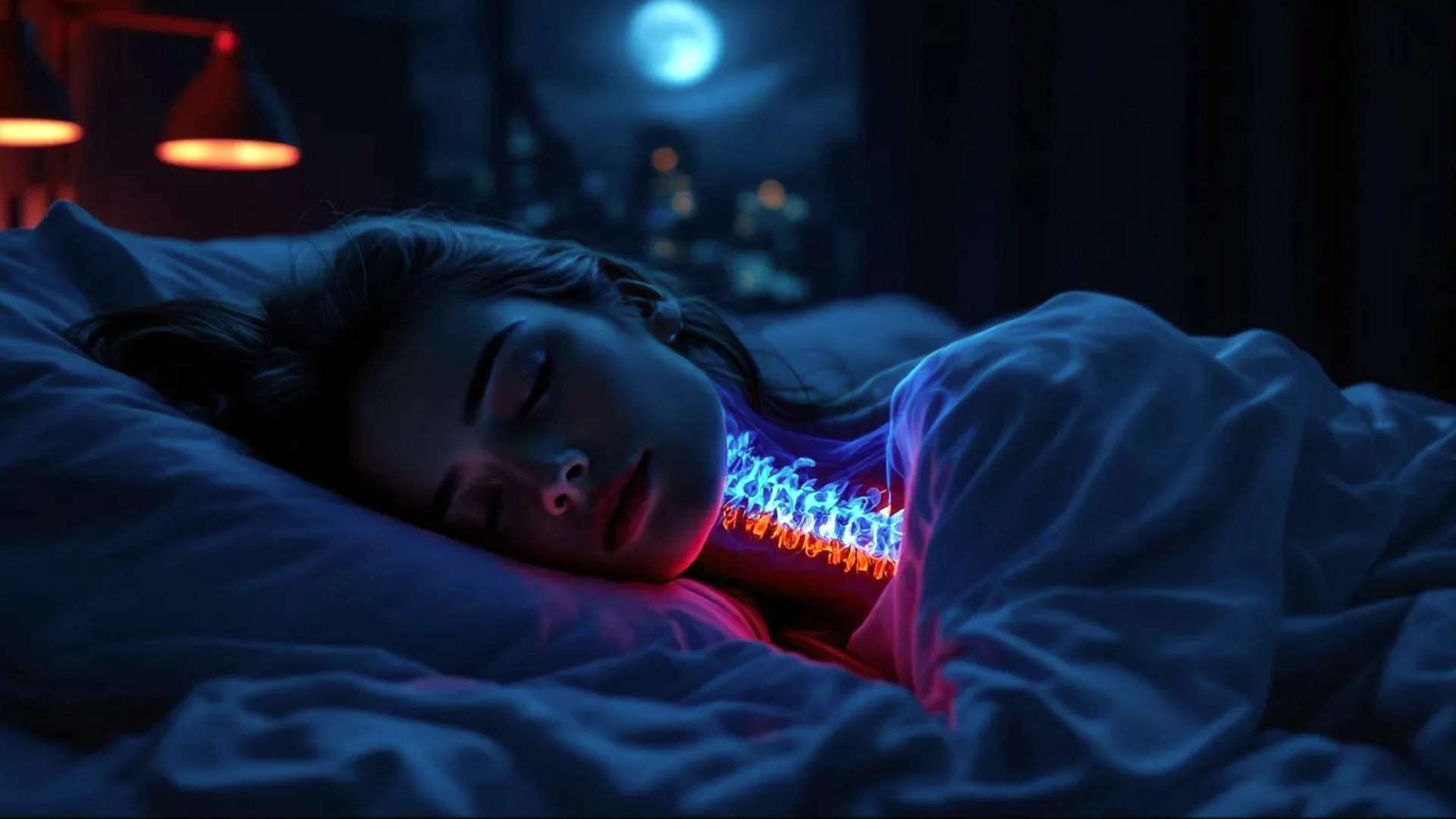
Sleep Health and Why it’s So Important
Sleep health refers to the quality, duration, and regularity of sleep necessary for optimal physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Good sleep health means consistently getting restorative sleep that allows the body and mind to function at their best. Poor sleep, on the other hand, can lead to a range of health problems, including chronic diseases, cognitive decline, and emotional instability.

Key Components of Sleep Health
- Sleep Duration
- Adults typically need 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
- Children and teenagers require more (8-12 hours, depending on age).
- Older adults (65+) may need slightly less (7-8 hours).
- Sleep Quality
- Refers to how restful and uninterrupted sleep is.
- Poor sleep quality (frequent awakenings, difficulty falling asleep) can be as harmful as insufficient sleep.
- Sleep Consistency
- Going to bed and waking up at the same time daily helps regulate the body’s internal clock (circadian rhythm).
- Irregular sleep schedules (e.g., shift work, late-night screen time) disrupt natural sleep patterns.
- Sleep Efficiency
- Measures how much time spent in bed is actually spent sleeping (ideally 85% or higher).
- Low efficiency (tossing and turning) indicates poor sleep health.
- Sleep Disorders
- Conditions like insomnia, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome (RLS), and narcolepsy can severely impact sleep health.
- Untreated sleep disorders increase the risk of chronic illnesses.
Why Is Sleep Health Important?
1. Physical Health Benefits
- Boosts Immune Function: Poor sleep weakens immunity, making the body more susceptible to infections.
- Supports Heart Health: Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
- Regulates Metabolism: Lack of sleep disrupts hormones (leptin & ghrelin), increasing obesity and diabetes risk.
- Promotes Muscle Recovery: Deep sleep is essential for tissue repair and muscle growth.
2. Mental and Cognitive Benefits
- Enhances Memory & Learning: Sleep helps consolidate memories and improves problem-solving skills.
- Improves Focus & Productivity: Well-rested individuals perform better at work and in daily tasks.
- Reduces Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases: Poor sleep is associated with Alzheimer’s and dementia.
3. Emotional and Psychological Benefits
- Regulates Mood: Sleep deprivation increases irritability, anxiety, and depression.
- Reduces Stress: Deep sleep lowers cortisol (stress hormone) levels.
- Improves Emotional Resilience: Good sleep helps manage emotions and reduces impulsive behavior.
4. Longevity and Disease Prevention
- People with healthy sleep patterns tend to live longer.
- Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of:
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Weakened immune response
- Mental health disorders
How to Improve Sleep Health
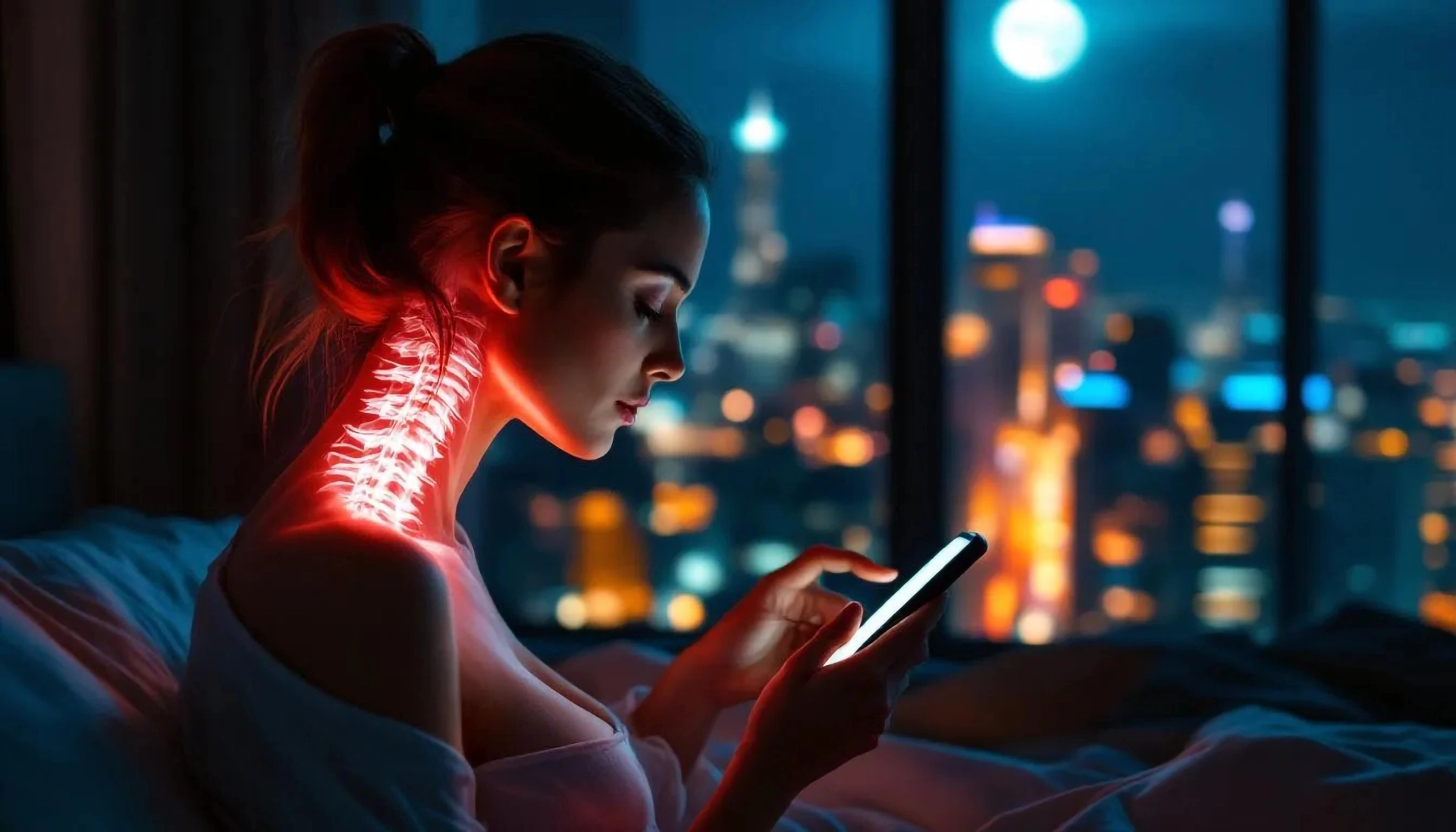

- 1. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule (even on weekends).
- 2. Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment (dark, cool, and quiet room).
- 3. Limit Screen Time Before Bed (blue light disrupts melatonin production).
- 4. Avoid Caffeine & Heavy Meals Before Bedtime.
- 5. Exercise Regularly (but not too close to bedtime).
- 6. Manage Stress (meditation, deep breathing, or journaling can help).
- 7. Seek Medical Help for Sleep Disorders (e.g., CPAP for sleep apnea, therapy for insomnia).
Conclusion
Sleep health is a cornerstone of overall well-being. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene can enhance physical health, sharpen mental clarity, stabilize emotions, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. By making sleep a priority, individuals can improve their quality of life and long-term health outcomes.